Everyone knows round brilliant cut diamond are among the most precious items on Earth, but only a few are aware of how long and tough the journey is. Its journey is filled with diligence and perseverance. From mining details to make the final cut, the entire journey takes billions of years. Diamonds rest for millions of years deep in the Earth before making the fascinating journey from the Earth's core to the Market.
These stones were formed approximately 3 billion years ago because of massive heat and pressure on carbon crystals. Each diamond has a different composition.
V.jayantilal & Co. offers genuine and alluring solitaires that are crafted with skill and precision and responsibly sourced.
Let's explore the memorable journey of a diamond from precious rock to market:
Exploring:
Your diamonds do not exactly seem the way they are in your jewelry. Diamonds are known as the hardest solids on Earth. They are formed under high heat and pressure beneath the land's surface. Some diamonds are believed to have originated millions of years ago, and they came closer to the surface after several volcanic activities. Some 'pipes' are formed, which are nothing but openings formed in the Earth's core, and some diamonds and other rare minerals, including kimberlite, are forced up to the surface of the Earth through these pipes. Most of the diamonds forced up through the Earth settle back into the kimberlite rocks in these pipes.
Naturally, diamonds occur in numerous exotic locations worldwide, such as Australia, Botswana, Canada, the Democratic Republic of Congo, Namibia, Russia, and South Africa, accounting for 80% of the world's diamond supply. Russia is a leading diamond ore and produces about 40% of the round brilliant cut diamond.
Mining:
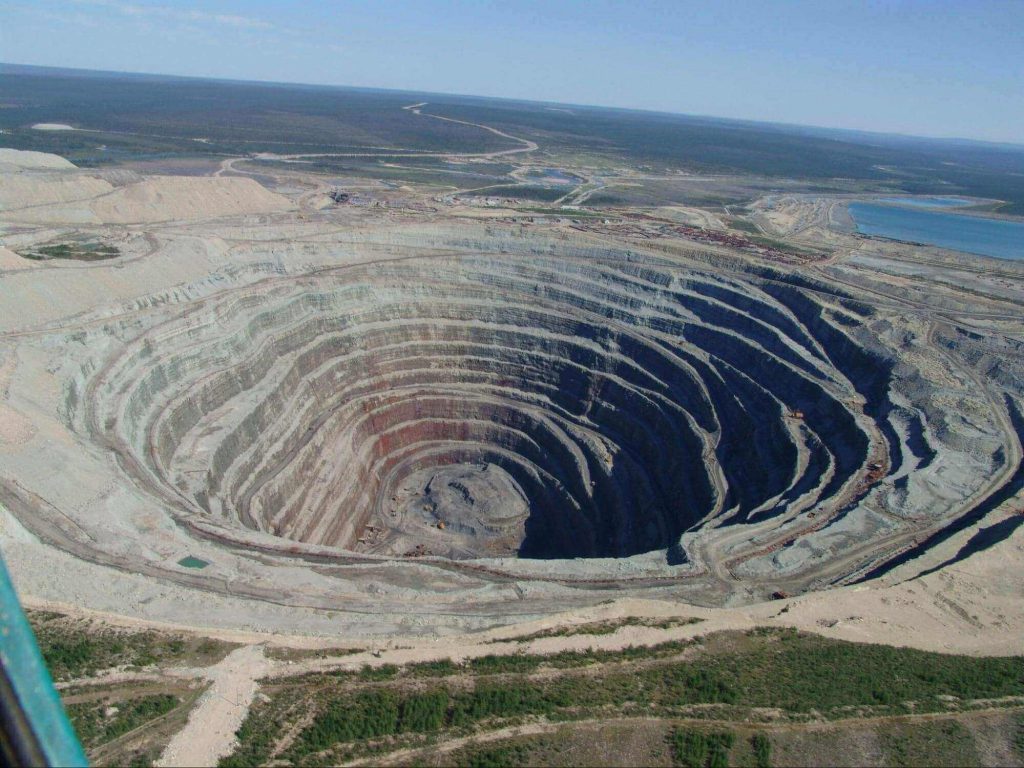

Once the exploration is done, mining operations are used to extract these minerals. Once the mining process has begun, it keeps going 24*7.
The different methods of mining:
Open Pit mining:
This mining method involves extracting rock or minerals from the Earth by their removal from an open pit. In other words, it dwells in mere surface excavation to extract the rock. This method is used when deposits of minerals are found along with kimberlite pipes or near the surface.
Underground mining:
This extraction method covers a range of methods used to mine gems, minerals, and ore bodies by tunneling underground. It is utilized when the pipes to be excavated are economically less feasible and are situated deep below the Earth's surface.
Marine mining:
This method of mining is done to extract minerals from the ocean bed. Through flexible pipes, crawlers suck gravel from the ocean floor. Another technique involves using a sizable ship-mounted drill to pluck the diamond-bearing pebbles. Today, due to advancements in technology, marine mining has also become commercially viable.
Alluvial Mining:
Alluvial mining is formed when minerals are eroded on riverbeds, and water currents have washed away kimberlite deposits. Miners build walls to expose the diamond-bearing ocean beds.
After extraction, the ore containing the rough diamonds undergoes many blasting, crushing, and processing stages, including advanced x-ray techniques, to liberate the diamonds. More than 250 tonnes of ore are required to produce one carat of raw diamonds. Rough diamonds weighing more than 120 million carats are extracted annually, but only around 25 percent of them are of gem quality.
India was considered the sole source of natural diamonds until the 18th century. The Golconda mines in Karnataka are where the world-famous Koh-i-Noor was mined and extracted.
Sorting:
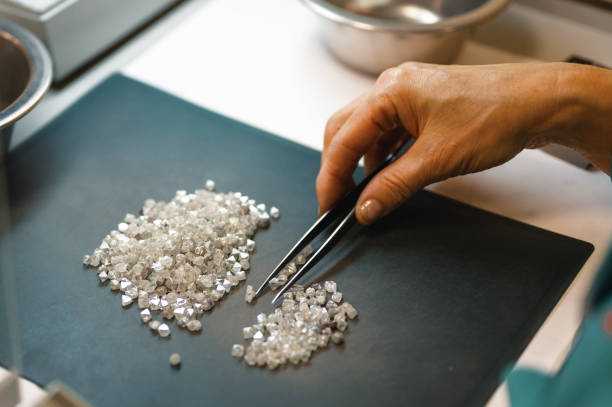

After the exploration and mining processes, the next step is to sort, classify, and value them. In this step, the rough diamonds are inspected and classified according to their size, shape, quality, and color for sale.
Cutting:
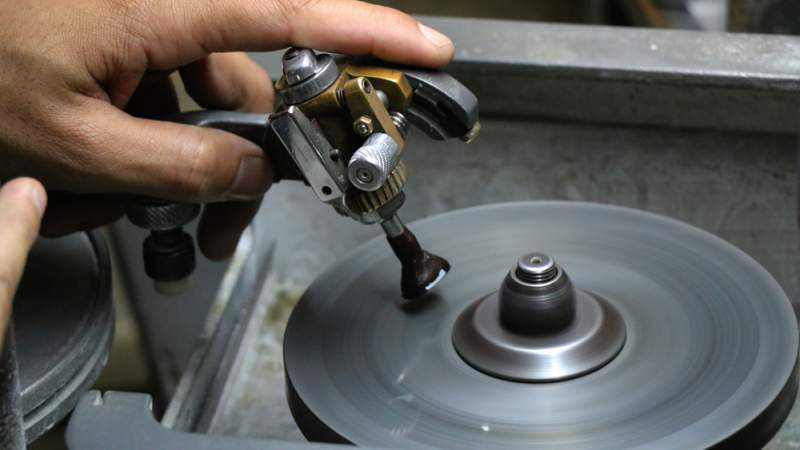

The next step for the rough diamond is cutting and polishing. Great skills with meticulous techniques are required in this activity. Diamonds are usually distributed to one of the main diamond cutting and trading centers in Antwerp, Mumbai, Tel Aviv, New York, Johannesburg, China, or Thailand.
The cut of the natural diamond determines the yield that is obtained. A round brilliant cut diamond has 57 facets. An excellent grade cut for princess, oval, and pear-shaped diamonds will ensure consistent, stunning sparkle and an even distribution of carat weight.
Surat is home to over 85% of the world's diamonds, cut and polished.
Polishing:
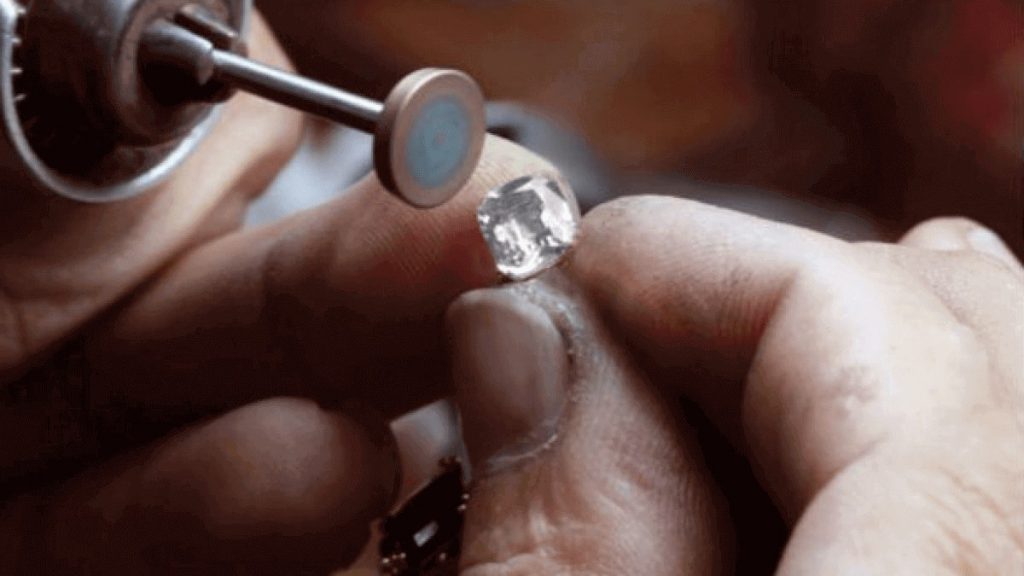

Polishing the last step of a diamond's metamorphosis from precious rock to sparkling gemstone is polishing. During the cutting and polishing process, the stone is repeatedly scanned to ensure that the cuts go according to design. Although some polishing processes are computerized, most are done by hand. First, the cutter uses cleaving, sawing, or laser cutting to separate the original rough into smaller, more workable pieces. The stone's edges are then ground away by the girdler using a technique called bruting to grind away the edge of the stone and provide its outline shape. Faceting follows, usually in two steps. Faceting follows, usually in two steps. The first 18 facets (that is: table, culet, bezel, and pavilion of a stone) are cut and polished by the blocker. The brilliant cuts and polishes the final 40 facets, including the star, upper girdle, and lower girdle. Finally, the cut gem is boiled in acid to remove dust and oil.
Grading:
The diamond's next stop is the laboratory, where they follow a step by step process of scrutiny. The stone is weighed first and then scanned to determine its precise measurements. Then Diamond's color, clarity, and finish are gauged under magnification. Even a slight scratch not visible to the naked eye could affect the grade. After this, a cut grade is assigned to the diamond, and a certification dossier number is granted and laser inscribed on it. The diamond is then returned with its certificate of being original. The certificate of the diamond is like its birth certificate, which provides critical information about the diamond.
Manufacturing:
Once the diamond gets its certificate, the next step is manufacturing the jewelry. The USA, India, China, Italy, Spain, Thailand, and Turkey have established solid reputations in jewelry manufacturing (industry.)
Retail:
Once the manufacturing process is completed, the diamond or the brilliant diamond jewelry is sold to the retailer. Asia, Australia, China, Europe, Japan, and the USA are the leading markets for this purpose.
For more than 40 years, Vjayantilal has been one of the leading diamond manufacturers in Surat, offering round brilliant cut diamond.